BPC 157 10MG
Couldn't load pickup availability
Description
BPC157 FROM PEPTIDECENTRAL.NET >99% PURITY LEVEL
- Composed of 15 amino acids, derived from the body protection compound in human gastric juice.
- May aid in the healing of wounds, including muscles, tendons, and ligaments (based on animal studies).
- Exhibits protective effects on organs and could prevent gastric ulcers.
- Potential applications in leaky gut, IBS, gastrointestinal cramps, and Crohn's disease.
- Shows promise in reducing pain and accelerating skin burn healing.
- Promotes reticulin, collagen formation, and angiogenesis through macrophage and fibroblast stimulation.
Local and Systemic Peptide Therapies for Soft Tissue Regeneration: A Narrative Review.
SEQUENCE:
Gly-Glu-Pro-Pro-Pro-Gly-Lys-Pro-Ala-Asp-Asp-Ala-Gly-Leu-Val
Disclaimer: These products are not approved by the FDA for the treatment of medical conditions. They are intended for research purposes only. PeptideCentral.net reserves the right to cancel orders from individuals attempting to use these products for weight loss or bodybuilding purposes. Must be 18 or older to order.
What Is BPC-157?
BPC-157: A Powerful Healing & Regenerative Peptide
BPC-157, a synthetic derivative of the Body Protection Compound (BPC) found in the digestive tract, is renowned for its healing and regenerative properties. This 15-amino acid peptide supports wound healing, tissue repair, and blood vessel growth, while also promoting gut health, reducing inflammation, protecting the brain, and enhancing joint, muscle, and tendon recovery. Research suggests its potential in treating injuries, accelerating recovery, and supporting overall wellness.
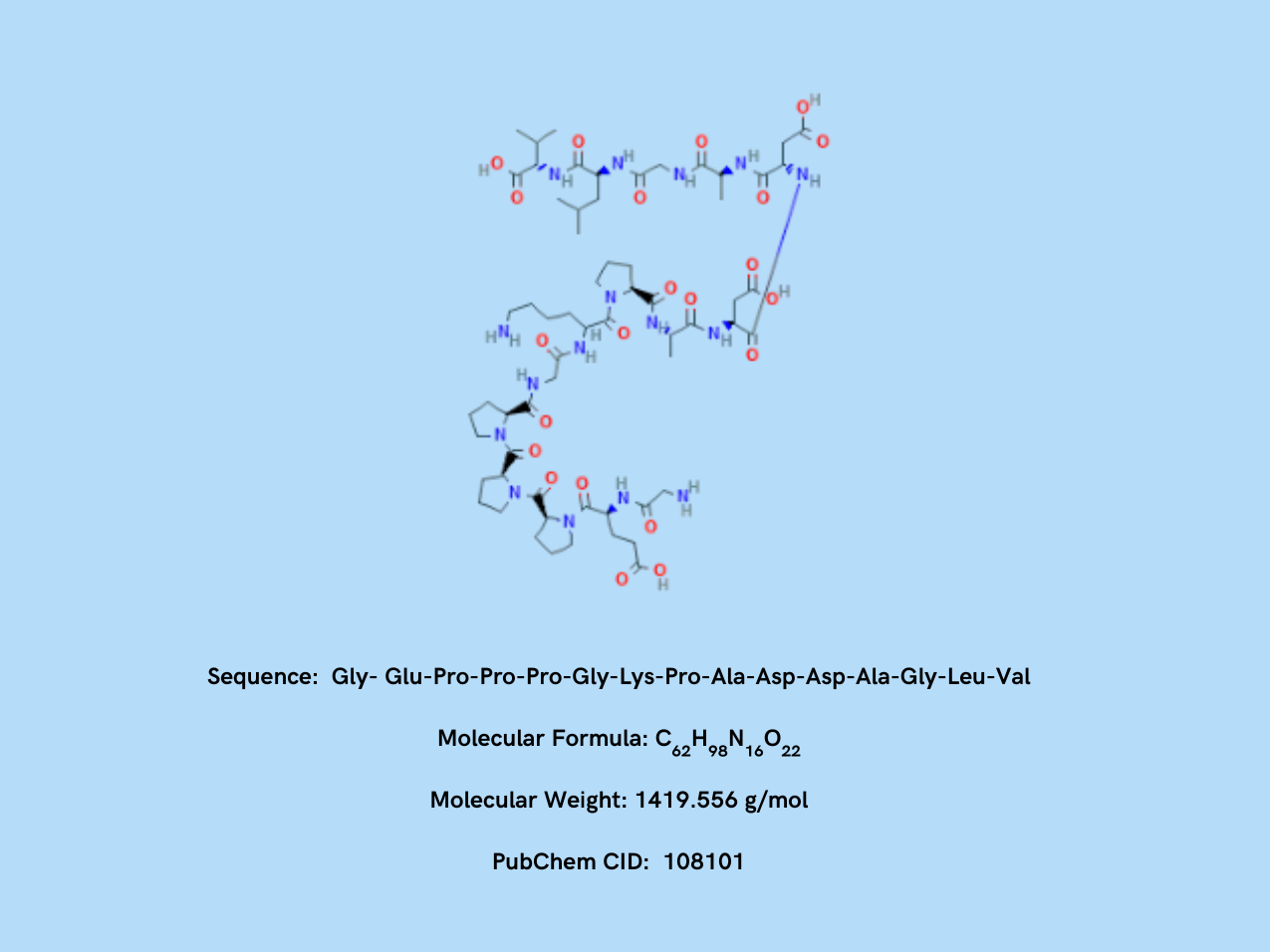
BPC-157 Peptide Structure
BPC-157 is a synthetic pentadecapeptide consisting of 15 amino acids, derived from the Body Protection Compound (BPC) found in human gastric juice. Its unique structure allows it to exhibit high stability and bioavailability, enabling it to promote tissue repair, wound healing, and anti-inflammatory effects. This peptide plays a crucial role in cellular regeneration, angiogenesis (blood vessel formation), and gastrointestinal protection, making it a promising compound in regenerative medicine.
BPC-157 Peptide Research
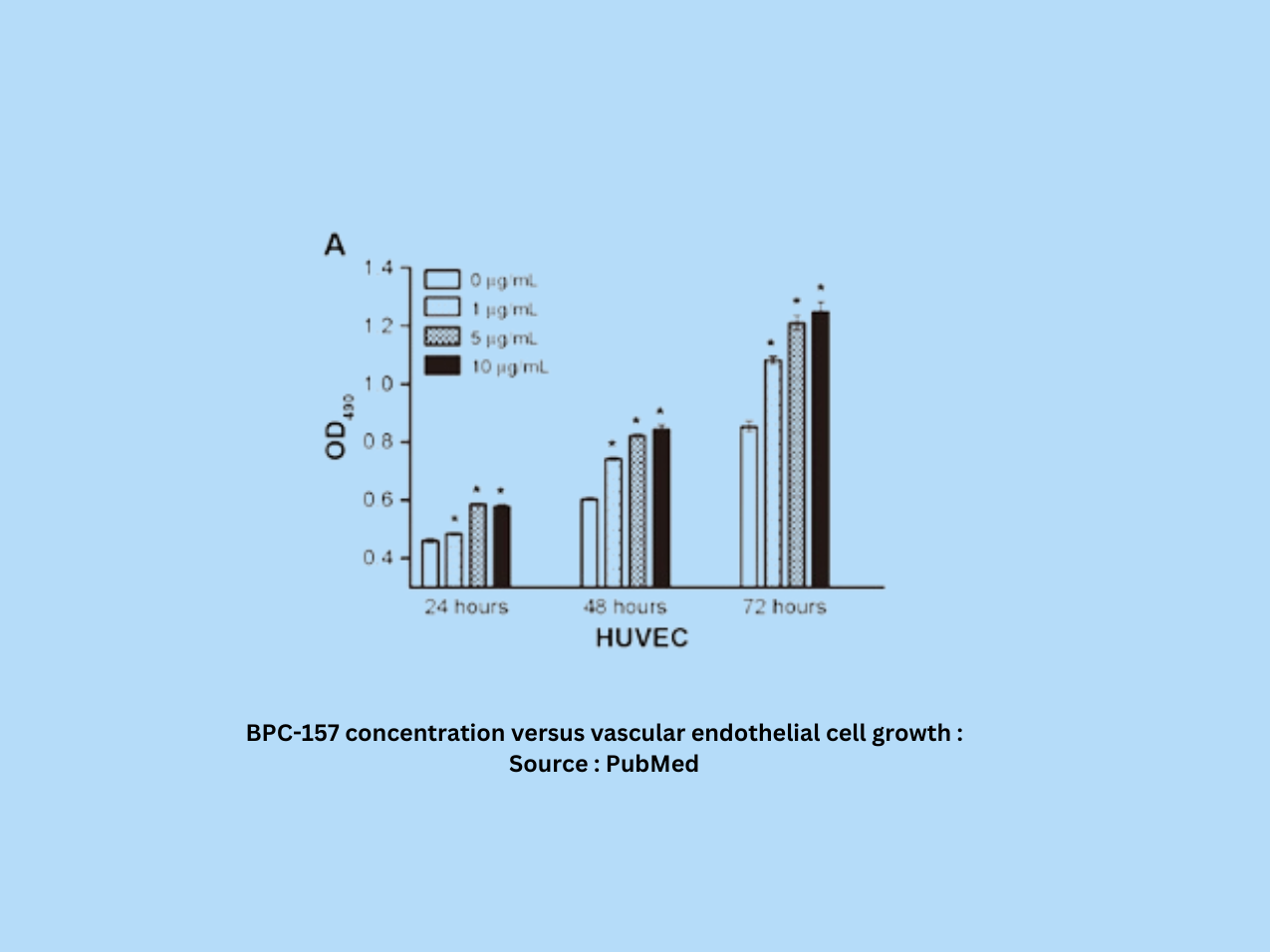
1. BPC-157 and Wound Healing
BPC-157 naturally occurs in the GI tract, where it plays a crucial role in maintaining the mucosal barrier. It helps protect underlying tissues from the harmful effects of gastric acid, bile, and digestive enzymes. Part of its function involves recruiting fibroblasts, which are essential for wound healing by producing extracellular matrix proteins like collagen and elastin.
2. Vascular Growth and Collateralization
BPC-157 is a potent angiogenic factor, meaning it enhances the growth and proliferation of endothelial cells (cells that form blood vessels). Studies show that BPC-157 increases the rate of collateral blood vessel growth, particularly in ischemic (low-oxygen) conditions. Research also suggests that BPC-157 stimulates VEGFR2, a receptor involved in the nitric oxide signaling pathway, which is crucial for endothelial cell growth and longevity.
3. BPC-157 and Tendon Healing
Given its role in fibroblast recruitment and blood vessel growth, BPC-157 has shown positive effects in animal models of tendon, ligament, bone, and connective tissue injuries. Poor blood supply in these tissues slows healing, but BPC-157 enhances fibroblast activity and collagen production, improving healing rates. Research suggests BPC-157 is more effective than bFGF, EFG, and VGF hormones in promoting tendon repair.
4. Antioxidant Properties
Studies indicate that BPC-157 neutralizes oxidative stress markers like nitric oxide and malondialdehyde (MDA). This makes it a powerful antioxidant, further supported by research suggesting its ability to reduce reactive nitrogen species in the digestive tract.
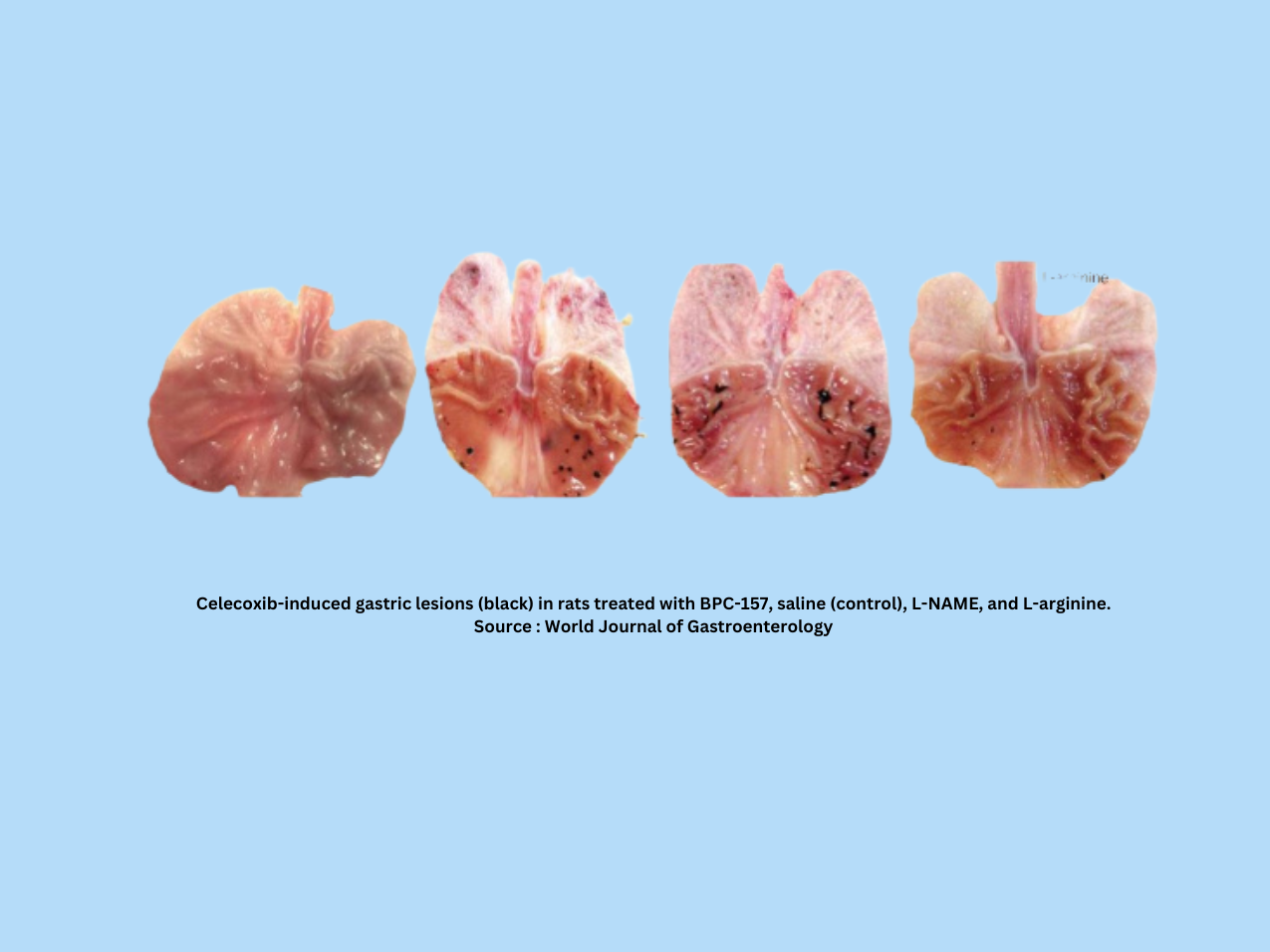
5. BPC-157 and Drug Side Effects
Many pharmaceutical drugs, like NSAIDs, cause serious side effects such as gastric bleeding and heart complications. BPC-157 has been shown to counteract NSAID-related damage. It also protects against QTc prolongation, a heart rhythm disorder caused by psychiatric medications. Additionally, BPC-157 helps mitigate side effects like colitis and somatosensory disturbances, making treatments more tolerable for patients.
6. BPC-157 and Bees
Colony Collapse Disorder (CCD) is a phenomenon where entire bee colonies experience rapid decline and eventual extinction. Some research suggests that environmental contamination may play a role, and BPC-157 has been explored as a potential protective agent due to its regenerative and antioxidant properties.
Future of BPC-157 Research
BPC-157 is actively being studied in cell culture and animal models, showing potential for wound healing, vascular growth, and regenerative medicine. Research suggests it may play a key role in angiogenesis, a process crucial for tissue repair, growth, and cancer development.
With minimal side effects, BPC-157 demonstrates moderate oral and high subcutaneous bioavailability in animal studies. However, its effects in humans remain under investigation. Currently, BPC-157 is available for educational and scientific research only and is not for human consumption.













